Following the signature of the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) in 1996, the French government assigned the Atomic Energy Commission (CEA) to develop a Simulation Program to guarantee the safety and reliability of nuclear weapons.
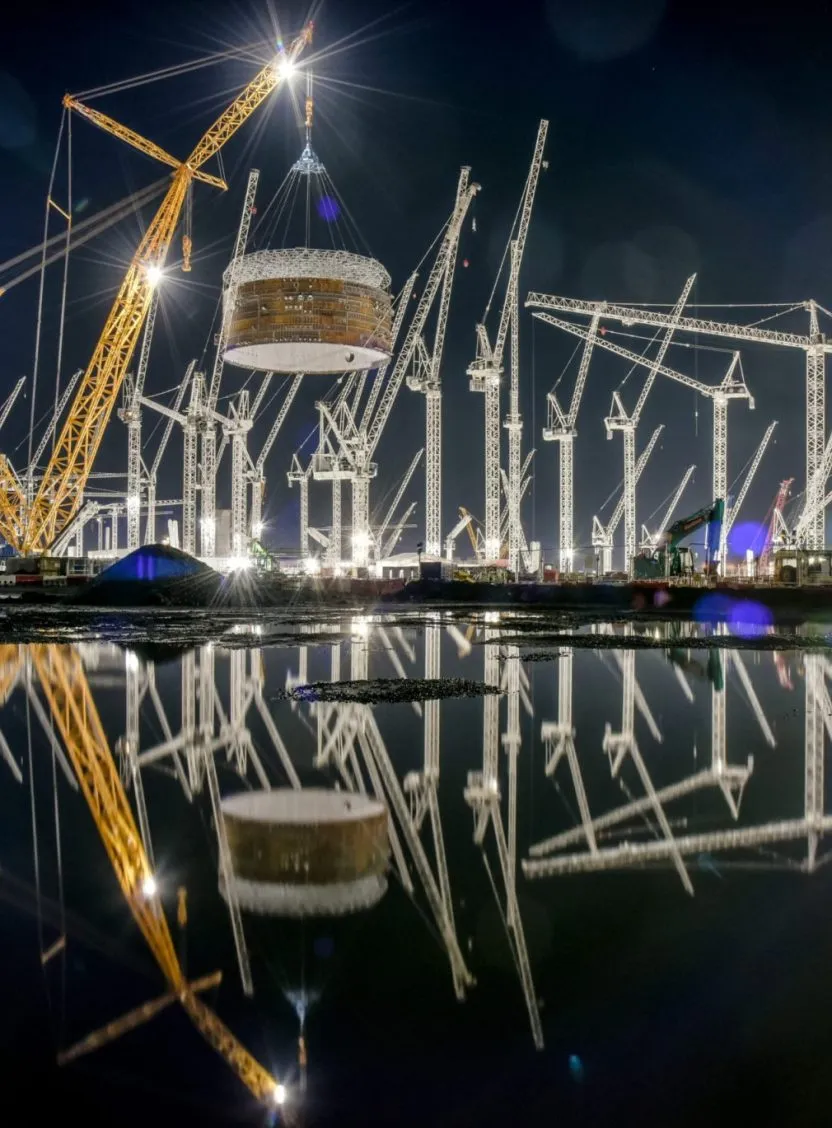
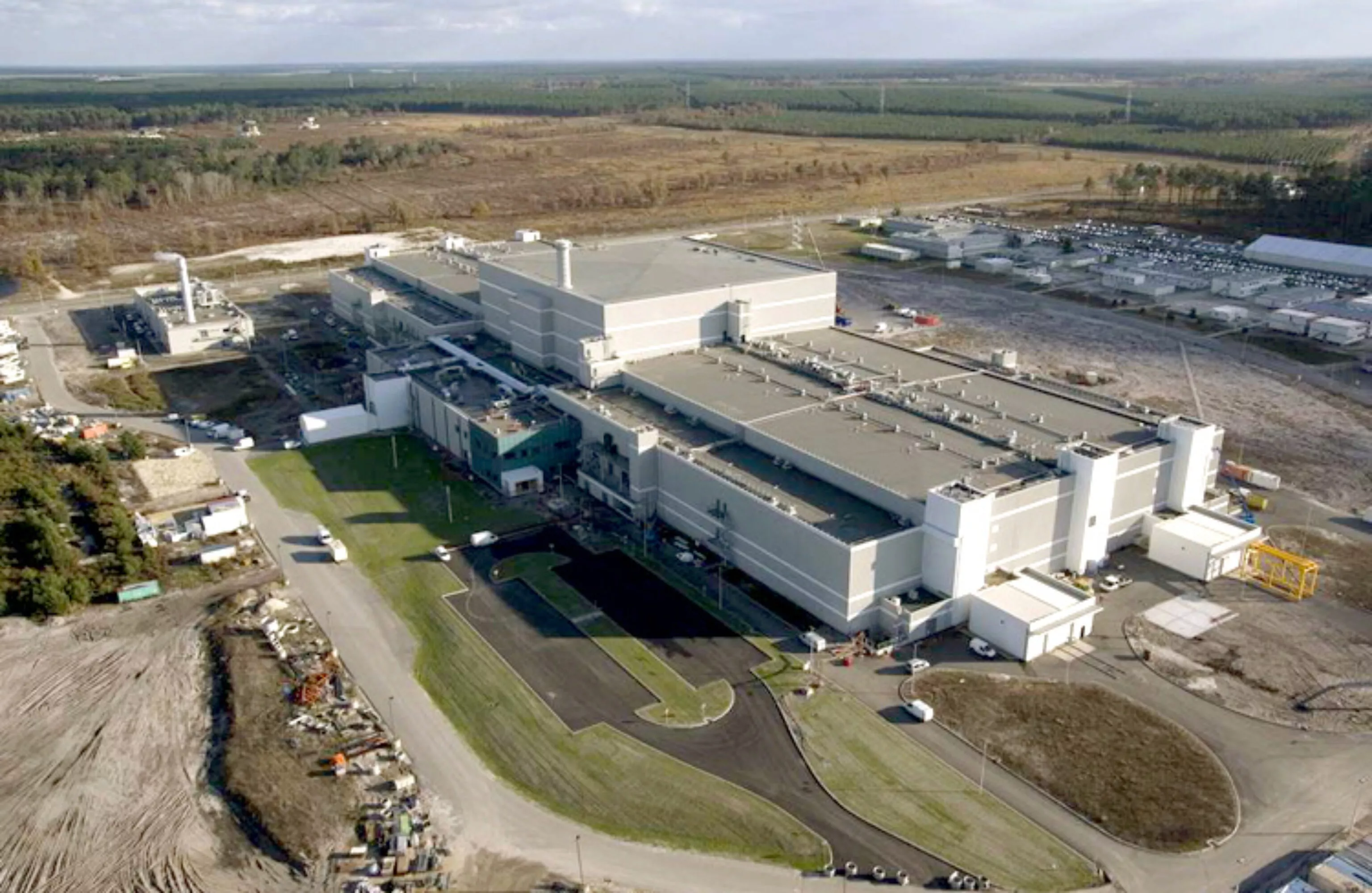
At the core of the Simulation Program, the Megajoule Laser facility (LMJ) located in the region of Bordeaux (southwestern France) is designed to study the behavior of microscopic target materials under extreme temperature and pressure conditions (similar to nuclear weapons).
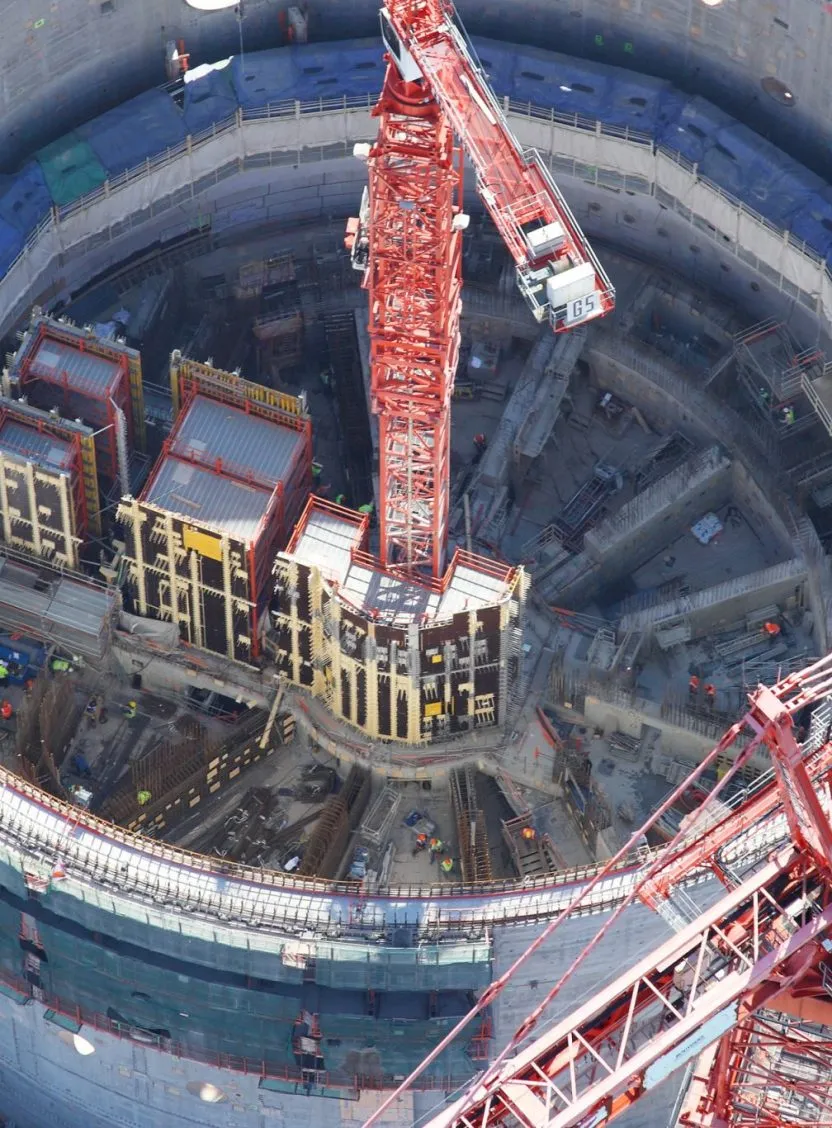
The LMJ building comprises 4 laser halls (each 128m long) sheltering 240 laser beams located at the four ends of the experimental hall. The experimental hall houses the experimental chamber positioned at the lasers’ focal point and consisting of a 350 ton aluminum sphere covered by a 40cm layer of borated concrete.